Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 14 outubro 2024
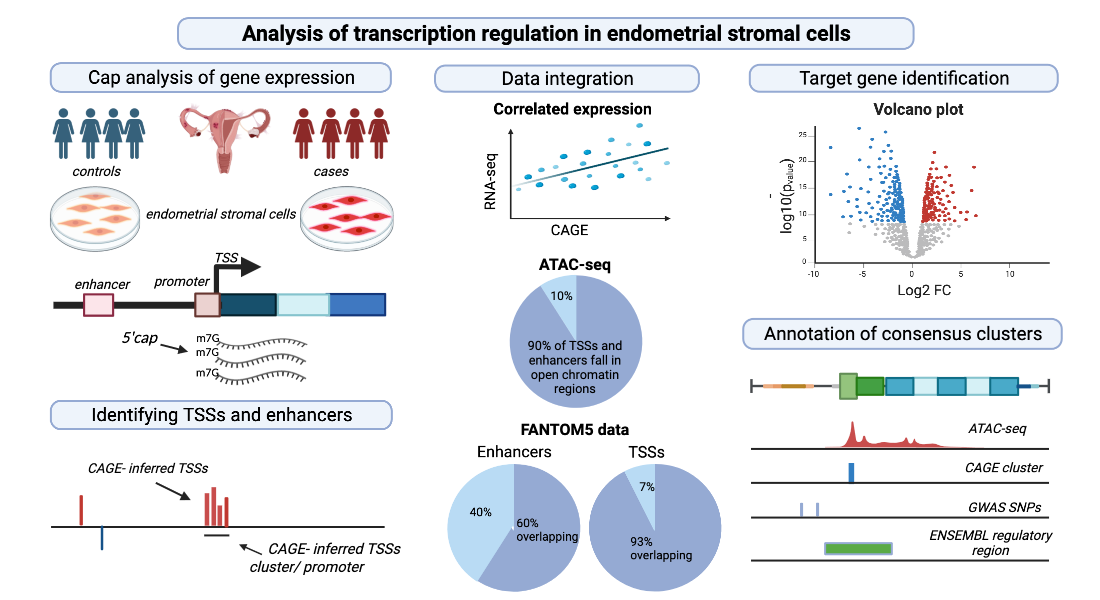
Identifying tissue-specific molecular signatures of active regulatory elements is critical to understanding gene regulatory mechanisms. In this study, transcription start sites (TSS) and enhancers were identified using Cap analysis of gene expression (CAGE) across endometrial stromal cell (ESC) samples obtained from women with (n = 4) and without endometriosis (n = 4). ESC TSSs and enhancers were compared to those reported in other tissue and cell types in FANTOM5 and were integrated with RNA-seq and ATAC-seq data from the same samples for regulatory activity and network analyses. CAGE tag count differences between women with and without endometriosis were statistically tested and tags within close proximity to genetic variants associated with endometriosis risk were identified. Over 90% of tag clusters mapping to promoters were observed in cells and tissues in FANTOM5. However, some potential cell-type-specific promoters and enhancers were also observed. Regions of open chromatin identified using ATAC-seq provided further evidence of the active transcriptional regions identified by CAGE. Despite the small sample number, there was evidence of differences associated with endometriosis at 210 consensus clusters, including IGFBP5, CALD1 and OXTR. ESC TSSs were also located within loci associated with endometriosis risk from genome-wide association studies. This study provides novel evidence of transcriptional differences in endometrial stromal cells associated with endometriosis and provides a valuable cell-type specific resource of active TSSs and enhancers in endometrial stromal cells.
Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus B-30892 can inhibit cytotoxic effects and adhesion of pathogenic Clostridium difficile to Caco-2 cells, Gut Pathogens

Streptomyces cell-free systems for natural product discovery and engineering - ScienceDirect
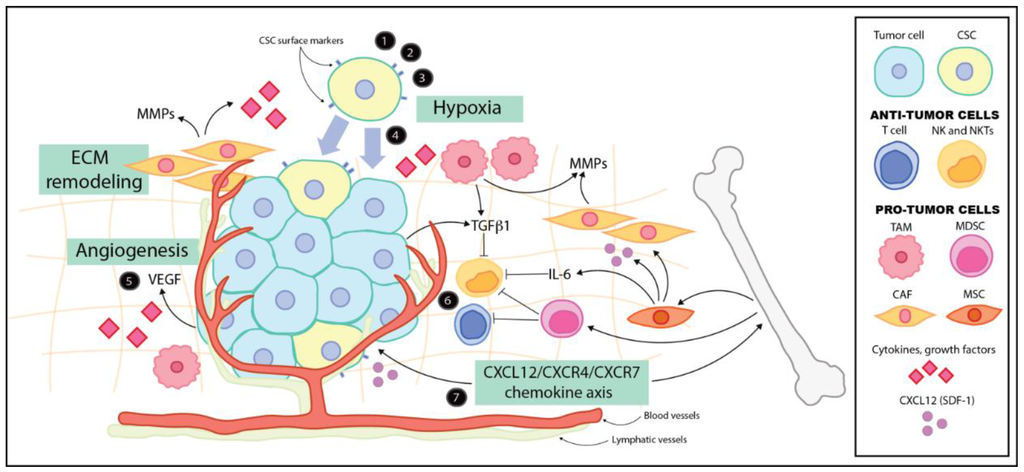
Cancers, Free Full-Text

Cells, Free Full-Text
Cells, Free Full-Text

The cell-free system: A new apparatus for affordable, sensitive, and portable healthcare - ScienceDirect
Cancers, Free Full-Text

An illustration of the full-duplex cell-free massive MIMO system.

Advancing synthetic biology through cell-free protein synthesis - ScienceDirect

PDF) Comparative separation methods and biological characteristics of human placental and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in serum-free culture conditions
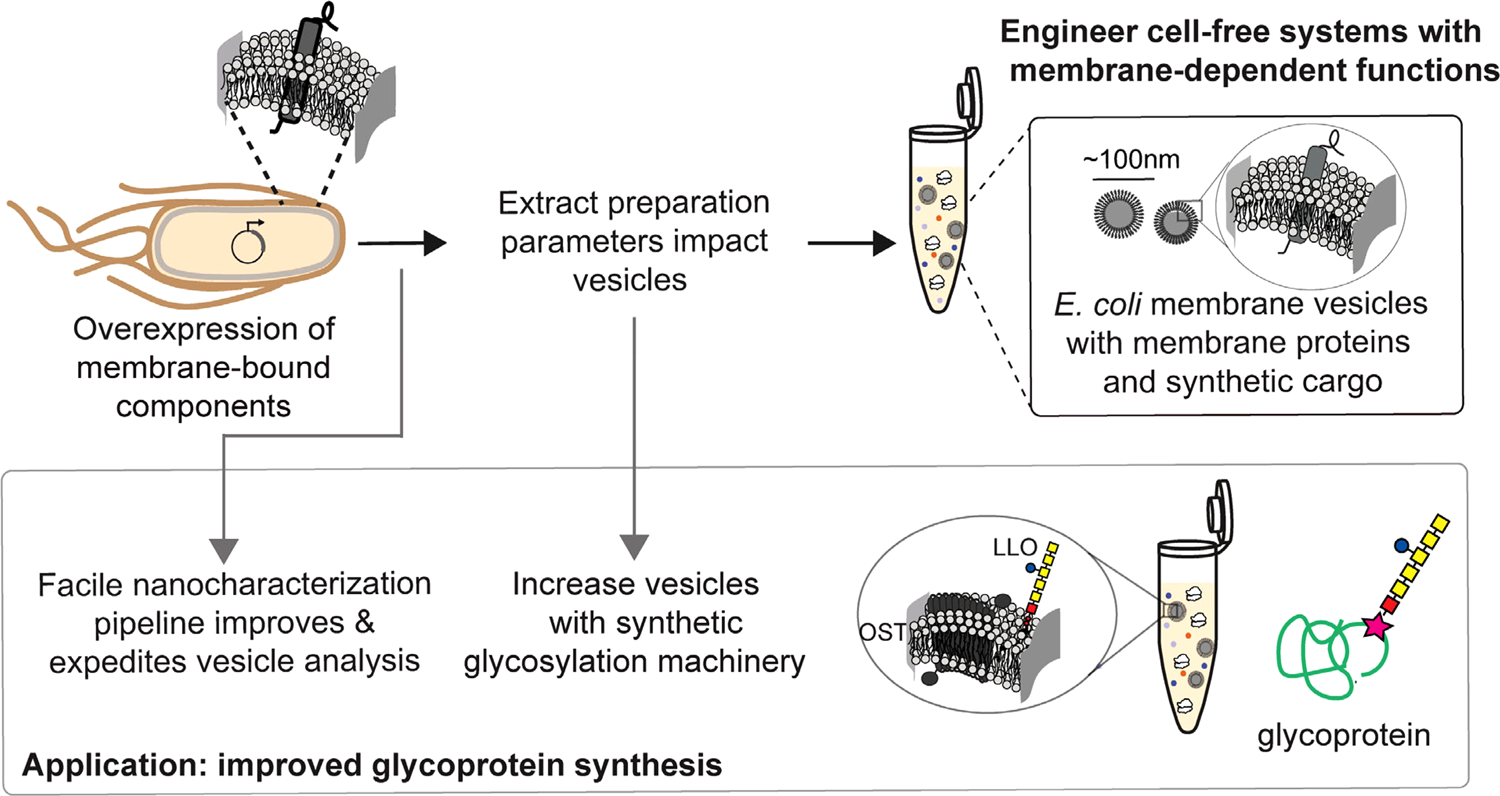
Improving cell-free glycoprotein synthesis by characterizing and enriching native membrane vesicles
Full-spectrum cell-free RAN for 6G systems: s
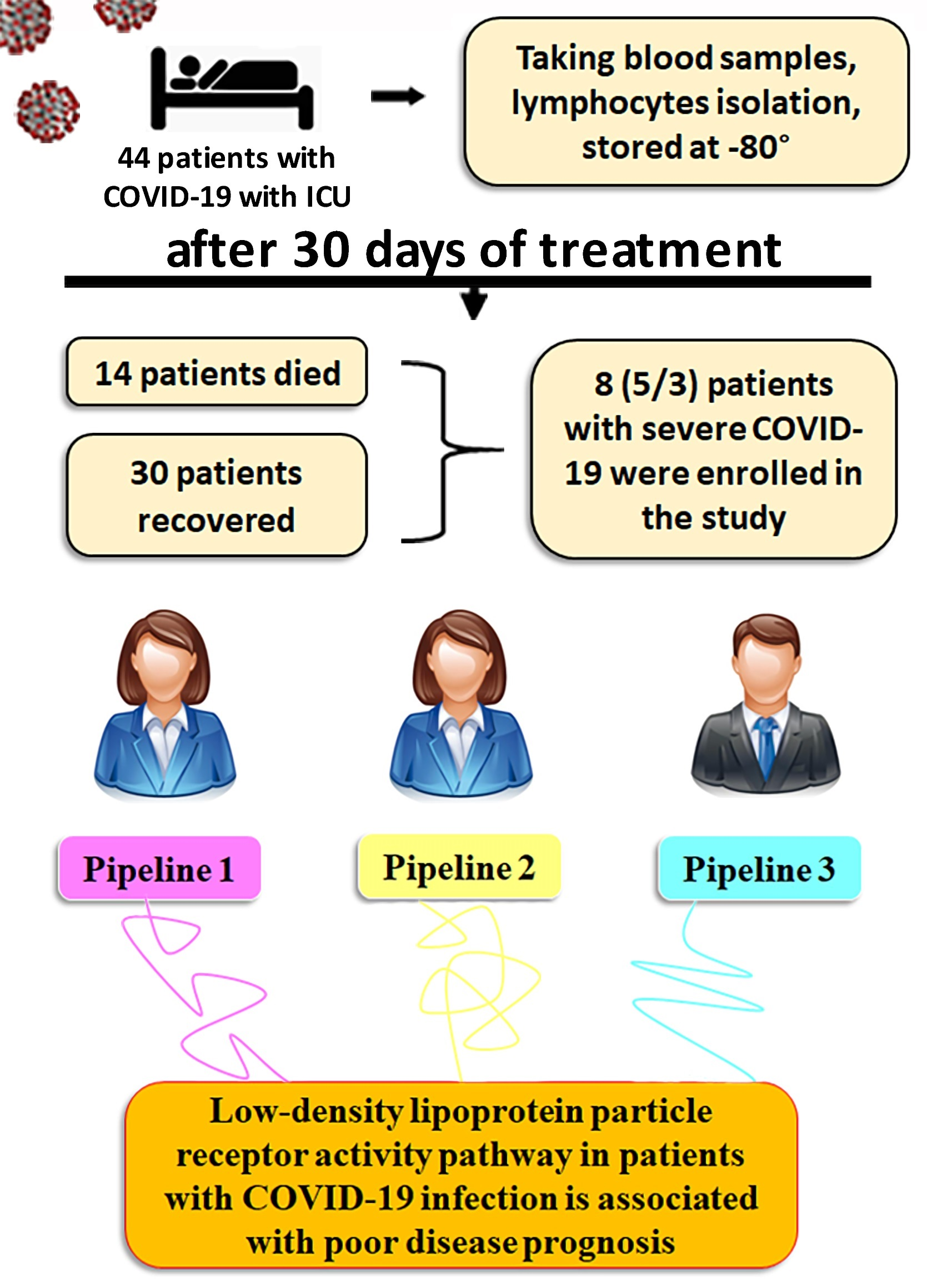
Cells, Free Full-Text
Cell-Free Protein Expression
Labile coat: reason for noninfectious cell-free varicella-zoster virus in culture. - Abstract - Europe PMC
Recomendado para você
-
 Morre o roqueiro Serguei aos 85 anos, no Rio de Janeiro - Verso14 outubro 2024
Morre o roqueiro Serguei aos 85 anos, no Rio de Janeiro - Verso14 outubro 2024 -
 Morre o roqueiro Serguei, aos 85 anos14 outubro 2024
Morre o roqueiro Serguei, aos 85 anos14 outubro 2024 -
 A network-guided protocol to discover susceptibility genes in14 outubro 2024
A network-guided protocol to discover susceptibility genes in14 outubro 2024 -
 Distribution of intersubject variability in the masked14 outubro 2024
Distribution of intersubject variability in the masked14 outubro 2024 -
 Paulo Ricardo: Fotos, últimas notícias, idade, signo e biografia14 outubro 2024
Paulo Ricardo: Fotos, últimas notícias, idade, signo e biografia14 outubro 2024 -
 Chay Suede - Wikipedia14 outubro 2024
Chay Suede - Wikipedia14 outubro 2024 -
 Spago, do chef Wolfgang Puck14 outubro 2024
Spago, do chef Wolfgang Puck14 outubro 2024 -
Sérgio Martins14 outubro 2024
-
 Metallica lança disco de vinil especial em homenagem a Chris Cornell14 outubro 2024
Metallica lança disco de vinil especial em homenagem a Chris Cornell14 outubro 2024 -
 Giselle MERINO, Pesquisador, professor, Doctor of Engineering, Universidade do Estado de Santa Catarina, Florianópolis, UDESC, Departamento de Design14 outubro 2024
Giselle MERINO, Pesquisador, professor, Doctor of Engineering, Universidade do Estado de Santa Catarina, Florianópolis, UDESC, Departamento de Design14 outubro 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Sanji cresceu em uma família de merda e os únicos que foram gentis com ele foram14 outubro 2024
Sanji cresceu em uma família de merda e os únicos que foram gentis com ele foram14 outubro 2024 -
 TEKKEN 8 CLOSED NETWORK UNUSED TEST CODE US PS5 for OCTOBER QUICK DELIVERY14 outubro 2024
TEKKEN 8 CLOSED NETWORK UNUSED TEST CODE US PS5 for OCTOBER QUICK DELIVERY14 outubro 2024 -
 Funko Vinyl Figure: Five Nights at Freddy's Toy Bonnie Collectible Figure, Multicolor : Toys & Games14 outubro 2024
Funko Vinyl Figure: Five Nights at Freddy's Toy Bonnie Collectible Figure, Multicolor : Toys & Games14 outubro 2024 -
 Motocross jérsei corrida 20/22/24/26/28 criança roupas infantis14 outubro 2024
Motocross jérsei corrida 20/22/24/26/28 criança roupas infantis14 outubro 2024 -
 DVD Anime Bleach Complete Series Vol 1-366 + 4 Movies English Audio Box Set14 outubro 2024
DVD Anime Bleach Complete Series Vol 1-366 + 4 Movies English Audio Box Set14 outubro 2024 -
 Prince of Persia: The Two Thrones : Artist Not Provided: Video Games14 outubro 2024
Prince of Persia: The Two Thrones : Artist Not Provided: Video Games14 outubro 2024 -
 A Pocket full of Sunshine — And the role definitely fits Hima! Look at how14 outubro 2024
A Pocket full of Sunshine — And the role definitely fits Hima! Look at how14 outubro 2024 -
publicidade Responder @aleatoria._.gabiii Ideias de skins do14 outubro 2024
-
 The best Soulslike games on PC in 202314 outubro 2024
The best Soulslike games on PC in 202314 outubro 2024 -
 anime mashle dublado ep 214 outubro 2024
anime mashle dublado ep 214 outubro 2024

