Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 20 setembro 2024
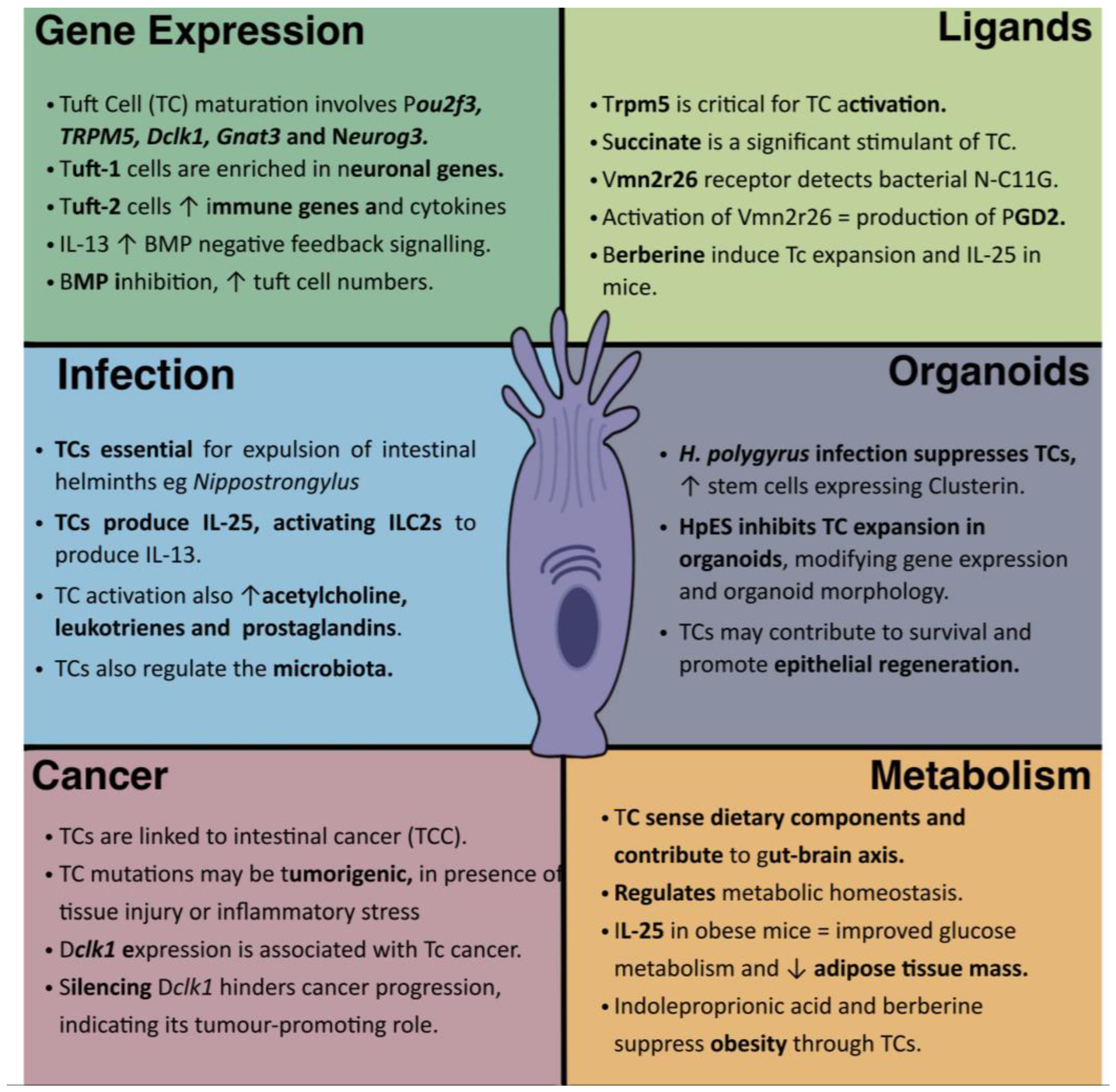
Tuft cells have recently emerged as the focus of intense interest following the discovery of their chemosensory role in the intestinal tract, and their ability to activate Type 2 immune responses to helminth parasites. Moreover, they populate a wide range of mucosal tissues and are intimately connected to immune and neuronal cells, either directly or through the release of pharmacologically active mediators. They are now recognised to fulfil both homeostatic roles, in metabolism and tissue integrity, as well as acting as the first sensors of parasite infection, immunity to which is lost in their absence. In this review we focus primarily on the importance of tuft cells in the intestinal niche, but also link to their more generalised physiological role and discuss their potential as targets for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders.
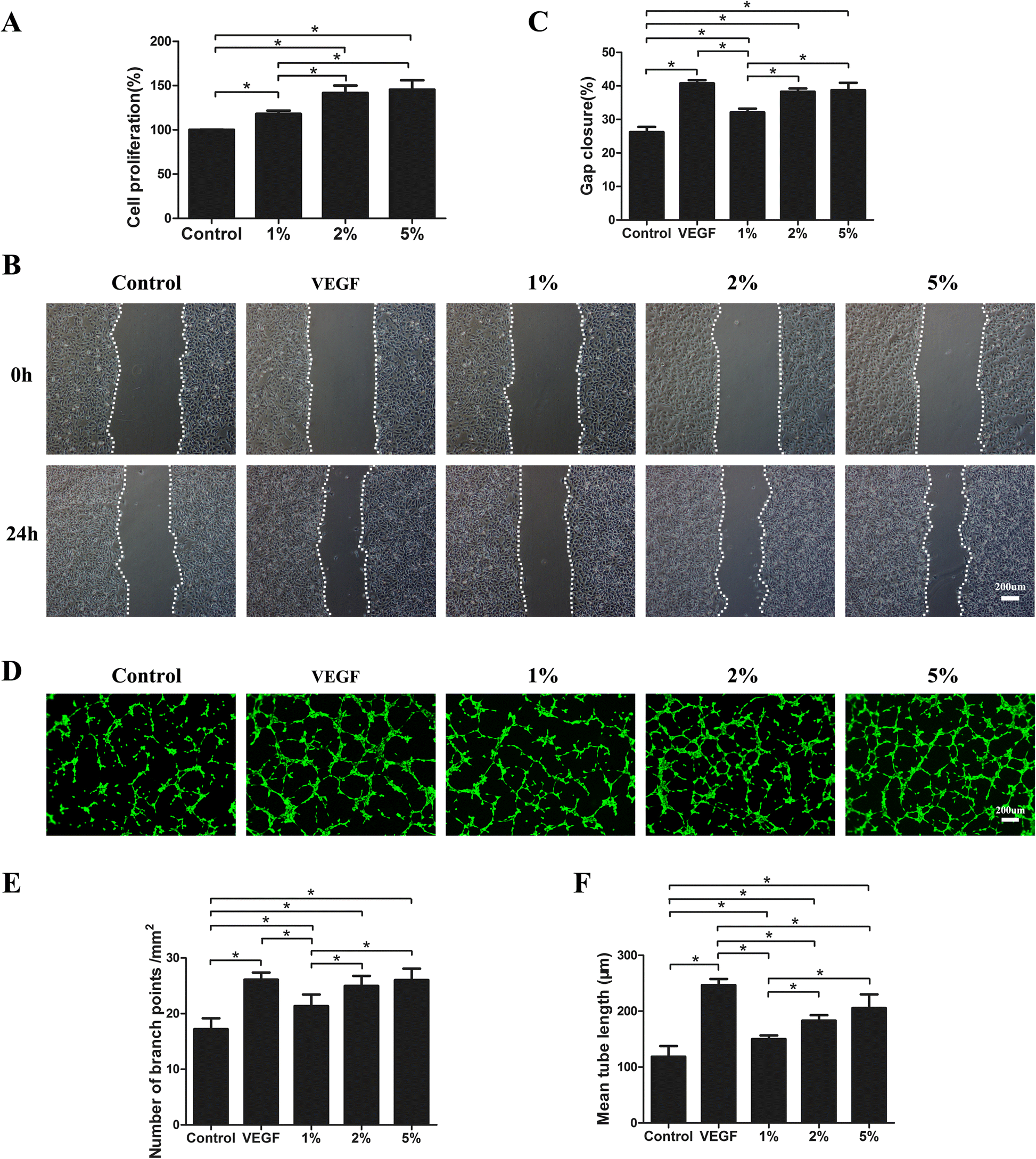
Fat extract promotes angiogenesis in a murine model of limb ischemia: a novel cell-free therapeutic strategy, Stem Cell Research & Therapy

Effect of calendar ageing on the cycle life of anode-free full-cells.

Cell-free DNA tissues of origin by methylation profiling reveals significant cell, tissue, and organ-specific injury related to COVID-19 severity - ScienceDirect
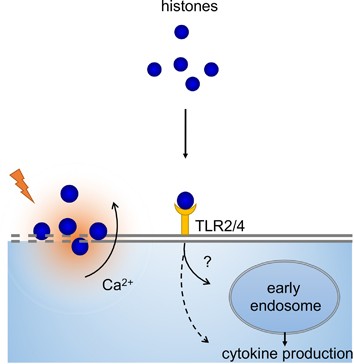
Extracellular histones, cell-free DNA, or nucleosomes: differences in immunostimulation

PDF) Comparative separation methods and biological characteristics of human placental and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in serum-free culture conditions
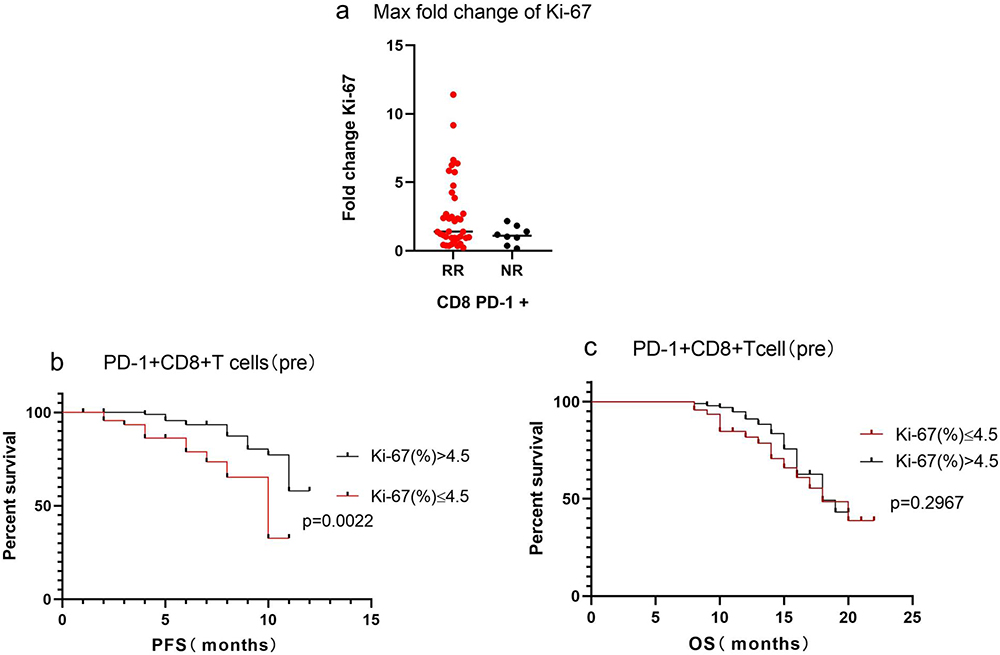
Cells, Free Full-Text
An illustration of the full-duplex cell-free massive MIMO system.
Rapid cell-free forward engineering of novel genetic ring oscillators

Cells, Free Full-Text
Recomendado para você
-
 Community Update #69. War Robots: Frontiers and our plans for the original WR : r/walkingwarrobots20 setembro 2024
Community Update #69. War Robots: Frontiers and our plans for the original WR : r/walkingwarrobots20 setembro 2024 -
 TIMEX INDIGLO WR 30M CR2016 CELL WATCH WHITE DIAL20 setembro 2024
TIMEX INDIGLO WR 30M CR2016 CELL WATCH WHITE DIAL20 setembro 2024 -
 Wild Rift News October 13, 202220 setembro 2024
Wild Rift News October 13, 202220 setembro 2024 -
 Chiefs' WR Justyn Ross reinstated; Andy Reid weighs in on return20 setembro 2024
Chiefs' WR Justyn Ross reinstated; Andy Reid weighs in on return20 setembro 2024 -
 Macrophage states: there's a method in the madness: Trends in Immunology20 setembro 2024
Macrophage states: there's a method in the madness: Trends in Immunology20 setembro 2024 -
 Perfect Cell by Mobigame - iPhone/iPad game trailer20 setembro 2024
Perfect Cell by Mobigame - iPhone/iPad game trailer20 setembro 2024 -
 How to Play Agar.io: 11 Steps (with Pictures) - wikiHow20 setembro 2024
How to Play Agar.io: 11 Steps (with Pictures) - wikiHow20 setembro 2024 -
 8849 Tank 2 Rugged Smartphone, 22GB+256GB Unlocked Rugged Phone with Projector, 6.79 4G Waterproof Cell Phone with Camping Light, 15500mAh 64MP Night Vision Android 13 Phone Unlocked, OTG/NFC : Cell Phones20 setembro 2024
8849 Tank 2 Rugged Smartphone, 22GB+256GB Unlocked Rugged Phone with Projector, 6.79 4G Waterproof Cell Phone with Camping Light, 15500mAh 64MP Night Vision Android 13 Phone Unlocked, OTG/NFC : Cell Phones20 setembro 2024 -
Bit Heroes Quest: Pixel RPG - Apps on Google Play20 setembro 2024
-
 War Robots: Frontiers Early Access is live now! - Pixonic20 setembro 2024
War Robots: Frontiers Early Access is live now! - Pixonic20 setembro 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Robotboy and Robotgirl by Robotboybestie on DeviantArt20 setembro 2024
Robotboy and Robotgirl by Robotboybestie on DeviantArt20 setembro 2024 -
 7 brinquedos educativos para crianças de todas as idades - Casa20 setembro 2024
7 brinquedos educativos para crianças de todas as idades - Casa20 setembro 2024 -
 Contando quebra-cabeça,9 em 1 Montessori Blocks Number Toys for Kids - Brinquedos montessori para crianças jogo contagem formas para crianças com mais 3 anos, : : Brinquedos e Jogos20 setembro 2024
Contando quebra-cabeça,9 em 1 Montessori Blocks Number Toys for Kids - Brinquedos montessori para crianças jogo contagem formas para crianças com mais 3 anos, : : Brinquedos e Jogos20 setembro 2024 -
 714 Rose Fish Stock Photos, High-Res Pictures, and Images - Getty Images20 setembro 2024
714 Rose Fish Stock Photos, High-Res Pictures, and Images - Getty Images20 setembro 2024 -
 Official Marcel Lotka (20) to join Borussia Dortmund - Get20 setembro 2024
Official Marcel Lotka (20) to join Borussia Dortmund - Get20 setembro 2024 -
 Desmantelo: candidato à presidência no Equador faz podcast fumando20 setembro 2024
Desmantelo: candidato à presidência no Equador faz podcast fumando20 setembro 2024 -
 Amma Png Sticker - Amma Png - Discover & Share GIFs20 setembro 2024
Amma Png Sticker - Amma Png - Discover & Share GIFs20 setembro 2024 -
 EMEELEKA - BLINDAO (Prod. Katylo)20 setembro 2024
EMEELEKA - BLINDAO (Prod. Katylo)20 setembro 2024 -
 Selling - ✓Exclusive Rewards PrimeGaming✓Roblox: Murder Mystery20 setembro 2024
Selling - ✓Exclusive Rewards PrimeGaming✓Roblox: Murder Mystery20 setembro 2024 -
 Visão Morreu o ator Lance Reddick da série The Wire e da franquia John Wick20 setembro 2024
Visão Morreu o ator Lance Reddick da série The Wire e da franquia John Wick20 setembro 2024